Information about the socio-economic state of the Republic of Abkhazia.
Today, the socio-economic model of the Republic of Abkhazia (RA) is as follows:
- by the achieved level of economic development, the RA is ranked as a country with a transitional economy;
- in terms of the development of productive forces – pre-industrial;
- by the degree of openness of the national economy – open;
- in areas of development – socially oriented;
- in terms of economic development – with an average level of GDP per capita.
The main strategic guideline of the socio-economic development of the Republic of Abkhazia is a transition to an innovative and socially oriented model of the state’s long term economic growth.
Population and employment
According to the information of the State Statistics Office, the population of Abkhazia stands at 243 936 people (as of January 1, 2016),
including:
• Urban population - 122 722 people (50.3 %)
• Rural population – 121 214 people (49.7%)
The number of the working population is 144,483 people. The number of people employed in different sectors of the economy is 42,313. 31,787 people are employed in the public sector and 10,056 - in the private sector.
For 2017, the average monthly salary of an employee in the Republic of Abkhazia is 10,316 rubles. As of March 1, 2018, the average monthly subsistence minimum per able-bodied resident of the Republic of Abkhazia is 6,702 rubles.
GDP and the state budget
According to the Department of State Statistics of the RA, the gross domestic product in the Republic of Abkhazia amounted to 30,292.2 billion rubles with a growth rate of 6% compared to the level of the previous year. In 2016, the GDP per capita was 124,180 rubles.
The state finance of the Republic of Abkhazia consists of:
1. State budget (the republican budget and local budgets — the city of Sukhum and the districts);
2. The system of state non-budgetary funds.
The main financial document of the Republic of Abkhazia is the State budget. The People’s Assembly — Parliament of the Republic of Abkhazia reviews, approves and monitors the execution of the State budget. Thus, according to the Law of the RA “On the State Budget of the Republic of Abkhazia for 2018”, the State budget for revenues is equal to 9,501.7 million rubles and for expenditures 9,607.9 million rubles.
In 2018, the revenues of the republican budget are planned to amount to 7,432.4 million rubles, including the financial help of the Russian Federation for the purpose of the socio-economic development of the Republic of Abkhazia (2,671.6 million rubles) and budget investments as part of the “Investment program of assistance to the socio-economic development of the Republic of Abkhazia for 2017-2019” (1,620.5 million rubles).
It should be noted that in recent years, the growth of own revenues in the structure of the consolidated State budget is to be observed. Thus, for example, in the last five years, the own revenues of the state budget of the RA have increased by 168.6%. These revenues are mostly generated by means of VAT, income tax, corporate tax and customs duties.
With regards to the remaining part of the consolidated State budget of the RA, it is formed by means of the funds that are received from the Russian Federation on the basis of intergovernmental agreements. These funds are received as financial help and also as part of the “Investment program of assistance to the socio-economic development of the Republic of Abkhazia for 2017-2019”.
The sectoral structure of the economy of the Republic of Abkhazia
Among the leading sectors of the economy of the Republic of Abkhazia, the following sectors can be pointed out:
· industry;
· tourism;
· agriculture;
· trade;
· services;
· construction;
· transport;
· the financial sector;
· communications, etc.
Industry
The Abkhazian industry was once highly developed, and it consisted of more than 500 enterprises. Yet, after the Patriotic War of the People of Abkhazia of 1992-1993 and the subsequent blockade that lasted for seven years and was brought about by the economic sanctions of the CIS countries, the Abkhazian industry went into decline. The main infrastructure facilities were destroyed, looted or fell behind technologically, which led to a significant outflow of qualified specialists. However, despite the abovementioned circumstances, the industry of Abkhazia is being revived.
Thus, currently, the industrial complex of the RA is one of the three main industries that form the GDP. In 2017, the volume of industrial production amounted to 3,541.1 million rubles. Today, more than a hundred industrial enterprises exist in Abkhazia out of which 87 are non-state enterprises. According to the data of the Department of State Statistics of the RA for 2017, 1,956 people are employed in this industry. The main part of the Abkhazian industrial enterprises is located in Sukhum (more than 40%).
The sphere of industrial production is represented by such industries as:
- processing (logging, production of veneer and furniture, production of fishmeal and fish oil);
- extractive (extraction of inert materials, limestone, coal);
- manufacturing (processing of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, production of paving slabs, blocks, concrete);
- food (production of bakery, alcoholic and non-alcoholic products);
- light (manufacture of garments);
- printing industry (production of printed products), etc.
It should be noted that of great importance to the Abkhazian economy are also the export-oriented wine-making, as well as fish processing industry. Thus, for example, the largest export item from the Republic of Abkhazia is wine production, which covered 75% of all exports in 2017. Along with countries like Spain, Italy, Georgia and France, Abkhazia is one of the five principle suppliers of wine on the Russian market. Only in 2016-2017, wine products worth 2.7 and 2.5 billion rubles were exported from the RA to the RF.
The production of honey, beer, adzhika, mineral waters and lemonades are represented in smaller volumes in Abkhazia. In 2012, as part of the Comprehensive plan of assistance to the socio-economic development of the Republic of Abkhazia for 2010-2012, the Sukhum milk factory was opened. Also, state investment in the processing industry is being planned.
The grown of construction as part of the financial help of the Russian Federation that aimed, mostly, at capital construction and the restoration of social infrastructure, has had a positive effect on the volume of internal production of construction material leading to the growth in the volume of the extractive industry.
The increase in the export of inert materials which are used in the construction of sports and infrastructure facilities as part of the preparation to the Sochi Olympics of 2014 has also had a positive effect on the volumes of production of the construction materials and the extractive industry. It should be noted that the export of inert materials from the Republic of Abkhazia to the Russian Federation is ongoing.
The power generation is a strategic part of the industry. It should be noted that all electricity generated in Abkhazia is being generated at the largest in the Caucasus hydroelectric station on the Ingur River. Given the water resources of Abkhazia, which consist of more than 13.5 million cubic meters of streamflow per year, the potential of hydropower, according to various estimates, exceeds 3.5 million kW. The development of hydropower of the republic is both a strategic and a promising task facing the country's leadership.
Tourism
One of the fastest growing and promising economic sectors in Abkhazia is tourism. Due to a number of competitive advantages (climate, nature, historical and architectural moments etc.), Abkhazian tourism has a solid place in the tourist markets attracting more than 1.5 million people to Abkhazia annually. According to the Ministry of the Economy of Abkhazia, the tourism industry accounts for up to a third of all tax revenues in the budget.
Educational tourism is one of the most sought after types of tourism in Abkhazia. On average, it accounts for more than 60% of the total tourist flow. Along with educational tourism, recreational tourism also develops successfully.
The majority of the tourists who come for the purpose of rest or medical treatment stay in the Gagra District, since more than 70% of the operational sanatorium and resort facilities are located in Gagra and Pitsunda. It should also be noted that New Athos and Gudauta are also becoming popular with tourists. In recent years, the tourist industry in these towns is characterised by rapid development.
Despite the relatively positive dynamics of the development of tourism in Abkhazia, due to a number of circumstances, the potential of the republic’s tourist sector is used only to a small degree. One of the most essential of the abovementioned competitive advantages of Abkhazia is the ecological cleanliness of the republic. Tourists are attracted by the humid warm climate, subtropical plant species and clear sea. There are many tourist centres, hotels, holiday homes and boarding houses located in the seaside area in Abkhazia. Most of them were built in Soviet times, and the history of some of them dates back to the period of Tsarist Russia.
In 2017, the total volume of resort and sightseeing services in Abkhazia amounted to 1,908.6 million rubles. Alone in 2017 more than 709 thousand people have visited the republican unitary enterprise “The New Athos Cave” and the Ritsa relic national park.
Agriculture
Abkhazia is a traditionally agrarian republic. Before the Patriotic War of the People of Abkhazia of 1992-1993, agriculture was focused on the use of the unique climatic conditions of Abkhazia to meet the needs of the USSR. Therefore, subtropical crops predominated, such as citrus fruit (tangerines, oranges), tea, tobacco, walnut, hazelnut, tung trees, etc. Corn, grapes and vegetables were also grown. After the war, due to the economic sanctions that were imposed on Abkhazia, foreign trade has stopped, and agriculture has become the means of survival. Herds of cattle and small ruminants have thinned out.
At present, the area of the Abkhazian land used by land users engaged in agricultural production is 397.3 thousand hectares. Among the main directions of development of modern agriculture are fishing (anchovy, horse mackerel) and crop production (citrus fruit, feijoa, persimmon – 7.2 thousand hectares; vineyards – 2.6 thousand hectares; hazelnut, etc.). Most of the agricultural products are exported to the Russian Federation and Turkey.
Trade
Trade occupies the first place in terms of GDP (in 2017), it accounts for over 25% of the total value added. In 2017, the total volume of wholesale in the Republic of Abkhazia amounted to 11,784.14 million rubles and retail – 17,109.5 million rubles. The following commodity groups prevail in the trade turnover of the Republic: petrol, construction materials, bread and bakery products, meat and poultry, milk and dairy products, vegetables, wheat flour, confectionery and so on. About 5% of the total number of people employed in different sectors of the economy work in this sector.
Services
The indicators of paid services to the population give a complete picture of the real standard of living of the population and include, in a generalised form, the results of the activities of the following services:
- domestic services;
- housing and communal services;
- passenger transport and communication services;
- services of the education system, culture, physical culture and sports;
- medical services;
- tourist and health-improving services;
- legal services.
The volume of paid services in recent years is growing rapidly over the entire Republic. According to the information of the State Statistics Office, for 12 months of 2017, the volume of paid services to the population, including the estimated sales of services provided by individual entrepreneurs, amounted to 7,077.9 million rubles.
The largest share in the structure of paid services is occupied by communication services and sanatorium and health services.
Construction
Construction is one of the most important sectors of the economy that forms the GDP of the Republic. A favourable factor of development of construction is the availability of large and diverse reserves of mineral resources, including marble, dolomite, granite, sand, brick-tiled clay and so on.
Both legal entities and individuals are employed in construction. On the whole, 230 companies are registered in the Uniform State Register of Enterprises and Organisations. This industry employs 1800 people. The majority of enterprises are non-governmental. The companies offer a variety of services, such as object design, construction, reconstruction of different types of buildings, the holding of necessary preparatory works, and finishing and roofing works. The main activity for the majority of construction companies is reconstruction. The volume of contract work performed by construction companies of Abkhazia for 2017 amounted to 2,690.6 million rubles.
Transport
All main types of transport exist in the Republic of Abkhazia. This industry is considered quite large for a small republic. More than 1.3 thousand people are employed in it.
Traditionally, automobile transport is considered the main type of transport. In 2016, it accounted for 22.3% of the total volume of the transported goods. The road network structure is axial: almost all highways of the republic are tied to the main highway running along the sea coast. The length of the republican roads is 473.8 km and of the roads of local importance — 1830.9 km.
Speaking of railway transport, the length of the railways in Abkhazia is 239 km. There is an electrified single-track coastal railway line Sochi-Sukhum-Gal with a branch Ochamchira-Tkuarchal (which is used to deliver exported coal to the port of Ochamchira). From 1992, railway traffic through Abkhazia is closed. The operation of the network is managed by the republican unitary enterprise “Abkhazian railway”.
In the times of the Soviet Union, the volume of the freight from the republic reached 12-14 million tons per year. Up to 18 pairs of passenger trains ran daily from Sukhum. All parts of the railway were electrified in the 1950-1960s.
Today, from the railway station in Sukhum, daily trains run in the direction of Sukhum-Moscow, Sukhum-Saint-Petersburg and Sukhum-Samara. Also in the summer, to make border crossing more convenient, an electric train runs between Gagra and Sochi.
There are two airports in Abkhazia. The Sukhum airport is located in 25 km from the capital. It has a runway with a length of 4 km, and it is designed to receive wide-body passenger liners and special purpose aircraft with a payload of up to 200 tons. The airport is open for weather conditions 364 days a year (the most favourable weather conditions on the territory of the former USSR). The Bambora airport is located in 40 km from Sukhum, near Gudauta. The runways are designed to receive civil aircraft and all-weather service of naval and transport aircraft. Yet, at present, passenger service through airports located in the territory of RA is not carried out.
Abkhazia has three seaports, including the Ochamchira port which was built for military purposes. The main seaport of Abkhazia is in Sukhum. Before the blockade connected with the Patriotic War of the People of Abkhazia of 1992-1993, cargo and passengers were transported from this port (the port’s cargo turnover reached 290,000 tons per year).
The seaports of Abkhazia are owned by the state. They are managed by the state company “Abkhazian shipping company”.
The financial sector
According to Article 140 of the Civil Code of the Republic of Abkhazia, the Russian ruble is the official currency of the Republic of Abkhazia.
Since Abkhazia is one of the states that have refused to have their own currency, the main source of accumulation of the country’s money supply is the balance of payment surplus.
The Republic of Abkhazia develops and implements a uniform state monetary policy in cooperation with the Cabinet of Ministers of the Republic of Abkhazia and the National Bank of the Republic of Abkhazia. The National Bank of the Republic of Abkhazia is a supervisory authority for banks and other credit institutions that are licensed by the National Bank of Abkhazia. The legal status and functions of the National Bank of Abkhazia are outlined in the Law of the Republic of Abkhazia “On the National Bank of the Republic of Abkhazia (Bank of Abkhazia)”.
The main indicators of the Bank of Abkhazia, which characterise monetary relations:
• refinancing rate of the Bank of Abkhazia – 12%;
• the interest rate on refinancing loans of the Bank of Abkhazia (taking into account the margin of 6 points to the annual rate) – 18%;
• the weighted average interest rate on interbank loans provided in rubles of the Russian Federation – 22%.
As of the start of 2018, the banking system of the Republic of Abkhazia is represented by the National Bank of the Republic of Abkhazia and 10 operating credit institutions (including 9 commercial banks and 1 settlement non-bank credit institution).
In recent years, according to the new political course, the banking system of the republic became actively involved in the process of economic recovery. It has become more socially oriented. Alone in 2015, the National Bank of the Republic of Abkhazia has developed several specialised tools to support individual segments of the economy.
1. Thus, for example, the Bank of Abkhazia together with the Ministry of Economy of the Republic of Abkhazia has developed a support mechanism for small businesses (SMEs). It envisaged the possibility of attracting the funds of the National Bank secured by the rights of claim on loans which were provided to the SMEs that have been selected in accordance with the Regulation of the National Bank of Abkhazia “On the order of providing loans to small businesses”. The ultimate beneficiaries of the loan were individual entrepreneurs and legal entities engaged in the priority sectors for the development of the RA economy – agriculture, tourism, industry, construction, etc. For SMEs engaged in agricultural activities, the interest rate was set at 6% per annum, and for those employed in other industries – at 12% per annum.
2. Along with the implementation of the program for the payment of pensions and social benefits through electronic means of payments, as well as the introduction of “payroll projects” by credit institutions in budgetary and commercial organisations of the republic, in October 2015, the National Bank of Abkhazia developed a specialised credit institutions refinancing loan for subsequent lending to individuals persons who receive wages, pensions and other types of payments through APRA cards.
3. In December 2015, the National Bank of Abkhazia has started the implementation of the target credit program for trade organisations. The ultimate beneficiaries of loans under this program are individual entrepreneurs and legal entities engaged in the retail or wholesale trade. The interest rate for trade organisations does not exceed 18% per year.
Speaking of foreign economic activity of the credit institutions of Abkhazia, due to the absence of wide recognition of the sovereignty of the Republic of Abkhazia, they work through the correspondent accounts in the banks of the Russian Federation. Accordingly, the conversion and further transfer to accounts in other countries are carried out on the above-mentioned accounts, upon prior request. On average, this procedure takes no more than one banking day.
In 2018, an Agreement on the integration of the national payment systems MIR and APRA has been signed. The integration of payment infrastructures is one of the priorities for the banking system of the Republic of Abkhazia. On the one hand, it will enable the citizens of the Republic of Abkhazia to use APRA cards on the territory of the Russian Federation, and on the other hand, to accept Mir cards on the territory of the Republic of Abkhazia. Intersystem integration will help to expand the geography of the acceptance of the cards issued by the member banks of the national payment system APRA. It will also become another link in creating a single payment space to ensure mutual acceptance of cards by various national payment systems.
Communications
Communications is one of the fastest growing industries in the RA. After the recognition of the Republic of Abkhazia by the Russian Federation (RF), the RA and RF have signed a Memorandum of cooperation in the field of communications. According to it, Abkhazia has received the territorial telephone code of the seventh world numbering zone in which Russia is located. Now for the fixed-line operator, the geographic code ABC - 840 is defined, for cellular operators the code DeF – 940 is to be used.
At the beginning of 2017, there were 63 communication enterprises in Abkhazia, including their divisions. The total revenue from the sale of products of this industry in the designated year amounted to 2,684.2 million rubles.
The following types of communication exist in Abkhazia:
1. Telephone communication (available in all district centres)
- digital telephony
- analog telephony
2. Cellular communication (available in 96% of the republic’s territory)
- AQUAFON GSM
- A-MOBILE
3. Broadband Internet (available in all regional centres)
International economic activity
According to the data of the State customs committee of the Republic of Abkhazia, the volume of foreign trade of the Republic of Abkhazia for 2017 amounts to 21 billion 444.1 million rubles, which is 3 billion 111.3 million rubles less than in 2016 (declined by 13%).
This includes:
export - 3 billion 594.0 million rubles, in 2016 – 5 billion 468.0 million rubles (recession rate - 34%);
import - 17 billion 850.1 million rubles, in 2016 - 19 billion 87.4 million rubles (recession rate - 7%).
In general, the positive dynamics of the growth of foreign trade turnover can be explained, first of all, by the positive changes in the economy of the republic. The solvency of the population constantly grows, and the level of consumption grows accordingly, and there is an increase in the number of tourists, etc.
The biggest foreign partner of Abkhazia is the Russian Federation whose share is more than 60% of the total turnover. Next is Turkey, Ukraine, China, Brazil, the Baltic countries, etc.
The most significant categories in the import structure are food, building materials, mineral products, equipment, household appliances and other goods. The list of products exported from Abkhazia, which mainly reaches the markets of the Russian Federation and Turkey, is traditionally dominated by products of the agro-industrial complex, mining and processing industries. Among it are such categories of goods as wine products, fish and fish products, citrus fruit, nuts, minerals, etc.
The natural resources of Abkhazia
Abkhazia is one of the richest countries in terms of natural resources. The republic has coal reserves (more than 5.3 million tons), peat, marble, granite, limestone, gabbro-diabase, chalk, tuff, barite, dolomite, lead, and various building materials. There are also small oil and gas fields on the shelf of Abkhazia. According to preliminary data, oil reserves range from 300 to 500 million tons. Most of the oil reserves are located at a distance of 10 kilometres from the coastline. There are also small gas fields.
The total area of agricultural land is 421.6 thousand hectares.
Abkhazia has one of the first places in the world in terms of water availability: there are more than 1.7 million cubic meters of streamflow per square kilometre per year. The total length of 120 rivers is more than 5 thousand kilometres. These include mostly the rapid mountain streams which offer the possibility of developing small hydropower.
The forests cover 57% of the territory (497 thousand hectares). The estimated total reserve of the forests is 114.5 million cubic meters.
Abkhazia has a huge amount of recreational resources. There are around 200 boarding houses, rest homes, sanatoriums, hotels, children’s health centres which are located in all climatic zones — from the subtropical to the alpine. In addition, there are more than 120 thermal and mineral springs.
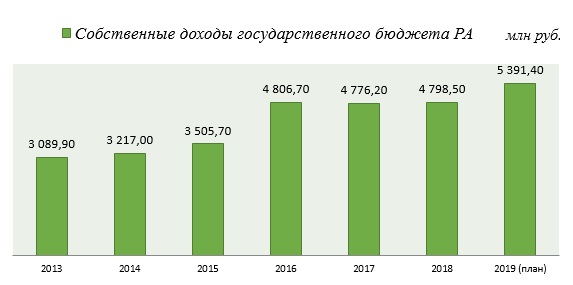
Следует отметить, что за последние годы наблюдается рост величины собственных доходов в структуре консолидированного Государственного бюджета. Так, например, собственные доходы государственного бюджета РА за период с 2014 по 2018 гг. увеличились на 49,2%. Эти доходы формируются, в основном, за счет НДС, подоходного налога, налога на прибыль и таможенных платежей.
Что касается оставшейся части консолидированного Государственного бюджета РА, то она формируется за счет средств получаемых от Российской Федерации на основе межгосударственных договоров. Эти средства поступают в качестве финансовой помощи, а также в рамках «Инвестиционной программы содействия социально-экономическому развитию РА на 2017-2019 гг.».
Отраслевая структура экономики РА
Среди ведущих отраслей экономики Республики Абхазия можно выделить следующие направления:
· промышленность;
· туризм;
· сельское хозяйство;
· торговля;
· услуги;
· строительство;
· транспорт;
· финансовый сектор;
· связь и т.д.
Промышленность
Некогда высокоразвитая промышленность Абхазии, насчитывавшая более 500 предприятий, после Отечественной войны народа Абхазии 1992-93 гг. и последующей семилетней блокады, вызванной экономическими санкциями стран СНГ, пришла в упадок. Основные фонды, инфраструктурные объекты, были разрушены, разграблены или отстали технологически. Однако, не смотря на вышеизложенные обстоятельства, промышленность Абхазии возрождается.
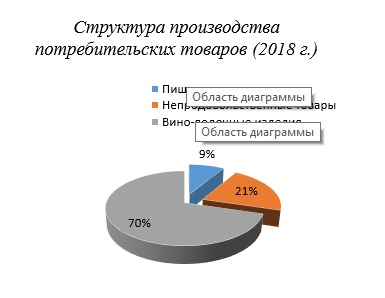
Так, в настоящее время, промышленный сектор РА входит в тройку базовых отраслей, формирующих ВВП. Объем промышленной продукции за 2018 г. составил 4 680,3 млн руб. На сегодняшний день в Абхазии насчитывается более 100 промышленных предприятий, в т.ч. 83 предприятия негосударственного сектора. По данным Управления государственной статистики РА за 2018 г. в отрасли заняты 2 006 человек. Основная доля промышленных предприятий Абхазии сосредоточена в г. Сухум.
Сфера промышленного производства представлена такими отраслями, как, например:
- перерабатывающая (заготовка леса, производство шпона и мебели, производство рыбной муки и рыбьего жира);
- добывающая (добыча инертных материалов, известняка, угля);
- обрабатывающая (обработка лома черных и цветных металлов, производство тротуарной плитки, блоков, бетона);
- пищевая (производство хлебобулочной, алкогольной и безалкогольной продукции, джемов, варенья, компотов);
- легкая (производство швейных изделий);
- полиграфическая промышленность (производство печатной продукции) и т.д.
Наиболее динамично в РА развиваются пищевая промышленность, производство строительных материалов и добывающая промышленность. Следует отметить важное значение для экономики Абхазии экспортоориентированной винодельческой, а также рыбоперерабатывающей промышленности. Так, например, самой крупной статьей экспорта из Республики Абхазия является винодельческая продукция, которая в 2018 г. покрыла 65% всего экспорта. Абхазия, наряду с такими странами, как Испания, Италия, Грузия и Франция является крупным поставщиком вина на российский рынок. Только за 2018 и 2017 гг. из РА в РФ было экспортировано винодельческой продукции на сумму 3,3 и 2,7 млрд руб., соответственно.
Небольшими объемами в Абхазии представлены: производство меда, пива, аджики, минеральных вод и лимонадов. В 2012 году в рамках Комплексного плана содействия социально-экономическому развитию Республики Абхазия на 2010-2012 гг., введен в эксплуатацию Сухумский молочный завод, планируются государственные инвестиции в перерабатывающую промышленность.
Рост объемов строительства в рамках финансовой помощи Российской Федерации направленной, в основном, на капитальное строительство и восстановление объектов социальной инфраструктуры, положительно отразился и на объемах внутреннего производства строительных материалов и привел к росту объемов добывающей промышленности.
К стратегической части промышленности относится производство электроэнергии. Необходимо отметить, что вся производимая в Абхазии электроэнергия генерируется на Ингурской гидроэлектростанции. Учитывая гидроресурсы Абхазии, более 13,5 млн. куб. м. речного стока в год, потенциал гидроэнергетики по разным оценкам превышает 3,5 млн кВт. Развитие гидроэнергетики республики является как стратегической, так весьма перспективной задачей, стоящей перед руководством страны.
Туризм
Одной из наиболее динамично развивающихся и перспективных отраслей экономики Абхазии является туризм. В силу ряда конкурентных преимуществ (климат, природа, памятники истории и архитектуры и т.д.), туристский продукт Абхазии занимает прочные позиции на рынке туристических услуг, привлекая в Абхазию свыше полутора миллионов человек ежегодно. Туриндустрия, вместе со смежными отраслями, по данным министерства экономики республики, приносит в бюджет до трети налоговых поступлений.
Самым востребованным видом туризма Абхазии является, познавательный, на долю которого, в среднем, приходится свыше 60% всего туристского потока. Наряду с познавательным, успешно развивается и рекреационный туризм.
Основная часть приезжающих с целью отдыха или лечения останавливаются в Гагрском районе, так как более 70% действующих санаторно-курортных объектов Абхазии расположены в городах Гагра и Пицунда. Также нельзя не отметить, нарастающий спрос со стороны туристов таких городов как Новый Афон и Гудаута, сфера туризма в которых за последние годы характеризуется быстрыми темпами развития.
Общий объем санаторно-оздоровительных и туристско-экскурсионных услуг за 2018 г. в целом по РА составил 1969,8 млн руб. В 2018 году в санаториях и учреждениях отдыха лечилось и отдыхало 131,7 тыс. чел., из них 128,0 тыс. чел. пользовались длительным лечением и отдыхом. Численность участников экскурсий в 2018 году составила 975,7 тыс. человек.
Несмотря на относительно положительную динамику развития туризма Абхазии, потенциал туристского продукта республики, в силу ряда обстоятельств, использован лишь на малую часть. В числе конкурентных преимуществ, перечисленных выше, ключевым звеном привлекательности Абхазии является экологическая чистота республики. Туристов привлекает влажный теплый климат, субтропические виды растений и удивительно чистое море. В Абхазии множество туристических центров, гостиниц, домов отдыха и пансионатов, расположенных в приморской зоне. Большинство из них построены в советское время, а некоторые историей своей восходят еще к периоду Царской России.
Сельское хозяйство
Абхазия – традиционно аграрная республика. До Отечественной войны народа Абхазии 1992-1993 гг. сельское хозяйство было ориентировано на использование уникальных климатических ресурсов Абхазии для удовлетворения потребностей СССР. Поэтому среди сельскохозяйственных культур преобладали субтропические: цитрусовые (мандарины, апельсины), чай, табак, грецкий орех, орех лесной, тунг и др. Выращивались также, кукуруза, виноград, овощи. После войны внешняя торговля в связи с экономическими санкциями, наложенными на Абхазию, прекратилась, и сельское хозяйство стало инструментом выживания. Сильно поредели стада крупного и мелкого рогатого скота.
В настоящее время, площадь земли РА, используемой землепользователями, занимающимися сельхозпроизводством равна 397,3 тыс. га. Среди основных направлений развития современного сельского хозяйства можно выделить рыболовство (хамса, ставрида) и растениеводство (цитрусовые, фейхоа, хурма – 7,1 тыс. га; виноградники – 2,6 тыс. га; орех лесной и т.д.). Большая часть производимой сельхозпродукции экспортируется в Российскую Федерацию и Турцию.
Торговля
Торговля занимает 1-е место по объему ВВП (2018 г.), на ее долю приходится почти 40% всей добавленной стоимости. В 2018 г. реализация продукции предприятиями оптовой торговли по Республике Абхазия составила 17 989,4 млн руб., а общий объем розничного товарооборота, включая общественное питание – 18 889,7 млн руб. В товарообороте республики превалируют следующие группы товаров: бензин, строительные материалы, хлеб и хлебобулочные изделия, мясо и птица, молоко и молочная продукция, овощи, мука пшеничная, кондитерские изделия и т.д. В данной отрасли работают порядка 6 % от всего числа занятых в отраслях экономики.
Услуги
Показатель платных услуг населению дает полное представление о реальном уровне жизни населения и включает в себя в обобщенном виде результаты деятельности следующих сфер услуг:
- бытовые услуги;
- жилищно-коммунальные услуги;
- услуги пассажирского транспорта и связи;
- услуги системы образования, культуры, физической культуры и спорта;
- медицинские услуги;
- туристско-экскурсионные и санаторно-оздоровительные услуги;
- услуги правового характера.
Объем платных услуг в последние годы в целом по республике растет быстрыми темпами. Согласно данным Управления государственной статистики РА за 12 месяцев 2018 г. объем реализации платных услуг населению с учетом оценки реализации услуг, оказанных индивидуальными предпринимателями составил 7 157,4 млн руб.
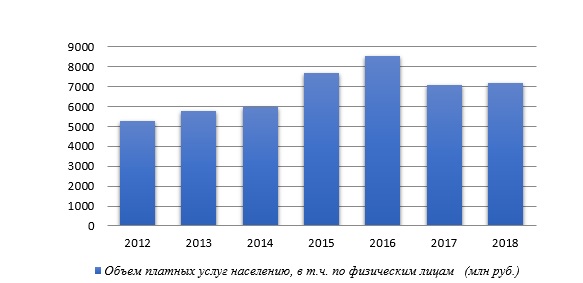
Наибольший удельный вес в структуре платных услуг занимают услуги связи и санаторно-оздоровительные услуги.
Строительство
Строительство одна из крупнейших отраслей, формирующих ВВП Республики. Благоприятным фактором развития строительства является наличие больших и разнообразных запасов минеральных ресурсов, в том числе мрамора, доломита, гранита, песка, кирпично-черепичной глины и т.д.
В строительстве заняты как юридические лица, так и индивидуальные предприниматели. Всего по ЕГРПО учтено 490 предприятий. В отрасли занято 1 716 человек. Основная часть предприятий относится к негосударственному сектору. Фирмы предлагают различные виды услуг, включающие в себя проектирование объектов, непосредственно строительство, реконструкцию сооружений различного типа, проведение всех необходимых подготовительных работ, отделочные, кровельные работы и др. Основная деятельность для большинства строительных организаций – капитальный ремонт. Объем подрядных работ, выполненный строительными организациями Абхазии, за 2018 г. составил 2 601,5 млн руб.
Транспорт
В Республике Абхазия имеются все основные виды транспорта. Эта отрасль считается довольно крупной для малой республики. В ней занято более 1,3 тыс. чел.
Основным, традиционно принято считать автомобильный транспорт. В 2018 году на него пришлось 27,2% от общего объёма перевезенных грузов. Структура дорожной сети — осевая: к главной магистрали, идущей вдоль морского побережья, привязаны почти все автодороги республики. Длина автодорог республиканского значения — 473,8 км, местного значения — 1830,9 км.
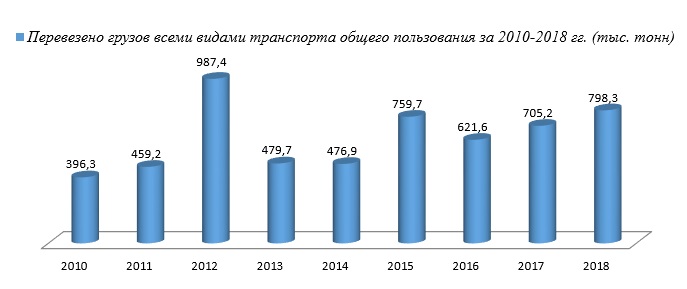
Что касается железнодорожного транспорта, то протяжённость железных дорог Абхазии составляет 239 км. Это электрифицированная однопутная приморская железнодорожная линия Сочи-Сухум-Гал с ответвлением Очамчыра-Ткурачал (используется для доставки экспортируемого угля в порт Очамчыра). Сквозное железнодорожное движение через Абхазию закрыто с 1992 г. Эксплуатация сети находится под руководством РУП «Абхазская железная дорога».
Во времена СССР объём грузоперевозок из республики достигал 12-14 миллионов тонн в год. Из Сухума ежесуточно курсировало до 18 пар пассажирских поездов. Все участки железной дороги были электрифицированы в 1950-60-х годах.
В настоящее время с вокзала г. Сухум регулярно отправляются поезда по направлению Сухум-Москва, Сухум-Санкт-Петербург, Сухум-Самара.
В РА имеются два аэропорта.Аэропорт г. Сухум расположен в 25 километрах от столицы, взлётно-посадочная полоса длиной 4 км, рассчитана на приём широкофюзеляжных пассажирских лайнеров и самолётов специального назначения грузоподъёмностью до 200 тонн; открыт по метеоусловиям 364 дня в году (наиболее благоприятные метеоусловия на территории бывшего СССР). Аэропорт Бамбора находится в 40 км от Сухума, около г. Гудаута. Взлётно-посадочные полосы рассчитаны на приём гражданских самолетов и всепогодное обслуживание военно-морской и транспортной авиации. Но, в настоящее время пассажирское сообщение через аэропорты расположенные на территории РА не осуществляется.
Абхазия располагает тремя морскими портами, включая построенный для военных нужд Очамчырский порт. Главный морской порт Абхазии - Сухум, откуда до блокады, связанной с Отечественной войной народа Абхазии 1992—1993 гг., осуществлялись перевозки грузов и пассажиров (грузооборот порта достигал 290 000 т в год).
Порты Абхазии находятся в государственной собственности. Эксплуатацию портов осуществляет государственная компания «Абхазское морское пароходство».
Финансовый сектор
Официальной валютой Республики Абхазия в соответствии со ст. 140 Гражданского Кодекса Республики Абхазия, является рубль Российской Федерации.
Учитывая, что Абхазия находится в числе стран, отказавшихся от собственной валюты, основным источником накопления денежной массы страны является положительное сальдо платежного баланса и финансовая помощь со стороны Российской Федерации.
Единую государственную денежно-кредитную политику Республики Абхазия разрабатывает и проводит во взаимодействии с Кабинетом Министров Республики Абхазия Национальный банк Республики Абхазия. Национальный банк Абхазии является органом надзора за банками и иными кредитными организациями, обладающими лицензиями Национального банка Абхазии. Правовой статус и функции Национального банка Абхазии определены Законом Республики Абхазия «О Национальном банке Республики Абхазия (Банке Абхазии)».
Основные показатели Банка Абхазии, характеризующие денежно-кредитные отношения:
• ставка рефинансирования Банка Абхазии – 12%;
• процентная ставка по кредитам рефинансирования Банка Абхазии (с учетом маржи 6 пунктов к годовой ставке) – 18%;
• средневзвешенная процентная ставка по межбанковским кредитам, предоставленным в рублях РФ – 22%;
Банковская система Республики Абхазия на начало 2019 года представлена Национальным банком Республики Абхазия и 10-ю действующими кредитными организациями (включая 9 коммерческих банков и 1 расчетную небанковскую кредитную организацию).
За последние годы, согласно новому политическому курсу, банковская система республики активно включилась в процесс подъема экономики. Она стала более социально-ориентированной. Только в 2015 г. Нацбанк РА разработал несколько специализированных инструментов для поддержки отдельных сегментов экономики.
1. Так, например, Банком Абхазии совместно с Министерством экономики РА был создан механизм поддержки субъектов малого предпринимательства (СМП), который предусматривал возможность привлечения средств Нацбанка под залог прав требования по кредитам, предоставленным СМП, отобранным в соответствии с Положением Нацбанка Абхазии «О порядке кредитования субъектов малого предпринимательства». Конечными получателями кредита стали индивидуальные предприниматели и юридические лица, занятые в приоритетных для развития экономики РА отраслях – сельском хозяйстве, туристической отрасли, промышленности, строительстве и т.д. Для СМП, занятых сельскохозяйственной деятельностью была определена процентная ставка в размере 6% годовых, для занятых в других отраслях – в размере 12% годовых.
2. Наряду с реализацией программы по выплате пенсий и социальных пособий с помощью электронных средств платежей, а также внедрением кредитными организациями «зарплатных проектов» в бюджетных и коммерческих организациях республики, в октябре 2015 г. Нацбанк Абхазии разработал специализированный кредит рефинансирования кредитных организаций для последующего кредитования ими физических лиц, получающих заработную плату, пенсии и другие виды выплат с помощью карт «АПРА».
3. В декабре 2015 г. Нацбанк РА начал реализацию целевой программы кредитования торговых организаций. Конечными получателями кредитов по данной программе являются индивидуальные предприниматели и юридические лица, занятые в сфере розничной или оптовой торговли. Размер процентной ставки для торговых организациях не превышает 18% в год.
Что касается внешнеэкономической деятельности кредитных организаций Абхазии, то они в силу отсутствия широкого признания суверенитета Республики Абхазия, осуществляют ее через корреспондентские счета в банках Российской Федерации. Соответственно, конвертация и дальнейший перевод на счета в других странах проводится по вышеупомянутым счетам, по предварительной заявке. Данная процедура занимает, в среднем, не более одного банковского дня.
В 2018 г. подписан Договор об интеграции национальных платежных систем «МИР» и «АПРА». Объединение платежных инфраструктур – одна из приоритетных задач для банковской системы Республики Абхазия, которая даст возможность, с одной стороны, гражданам Республики Абхазия использовать карты «АПРА» на территории Российской Федерации, а с другой – обслуживать карты «Мир» на территории Республики Абхазия.
К настоящему времени процесс интеграции завершен. Таким образом, созданы условия для расширения географии обслуживания карт, эмитированных банками-участниками НПС «АПРА».
Связь
Связь является одной из самых динамично развивающихся отраслей в РА. После признания Республики Абхазия со стороны Российской Федерации, в 2009 году между РФ и РА был подписан Меморандум о сотрудничестве в области связи. По его условиям Абхазия получила территориальный телефонный код седьмой всемирной зоны нумерации, в которой расположена Россия. Теперь для оператора фиксированной связи определен географический код АВС — 840, для операторов сотовой связи предполагается использование кода DeF — 940.
На начало 2019 г. в Абхазии насчитывалось 61 предприятие связи, в т.ч. их подразделения. Общая выручка от реализации продукции данной отрасли в 2018 году составила 2 653 млн. руб.
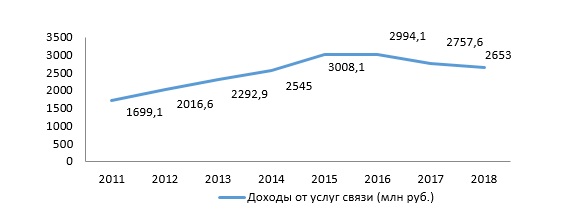
В Абхазии имеются следующие виды связи:
1. Телефонная связь (доступна во всех районных центрах)
- цифровая телефония
- аналоговая телефония
2. Сотовая связь (доступна на 96% территории республики)
- AQUAFON GSM
- A-MOBILE
3. Широкополосный интернет (доступен во всех районных центрах).
Внешнеэкономическая деятельность
По данным Государственного таможенного комитета Республики Абхазия объем внешней торговли Республики Абхазия за 2018 год составил 23 млрд. 704,8 млн. руб., что на 2 млрд. 260,7 млн. руб. больше, чем за 2017 год (прирост 10,5%). В том числе:
· экспорт – 5 млрд. 161,8 млн. руб.; прирост по сравнению с 2017 г. составил 43,6%;
· импорт – 18 млрд. 543,0 млн. руб.; прирост по сравнению с 2017 г. составил 3,9%;
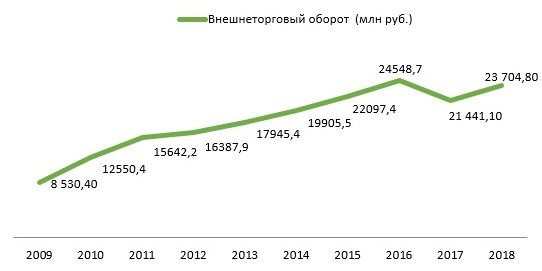
В целом, положительная динамика роста внешнеторгового оборота обусловлена прежде всего позитивными изменениями в экономике республики. Постоянно увеличивается платежеспособность населения, соответственно растет объем потребления, наблюдается увеличение туристических потоков и т.д.
Важно подчеркнуть, что по итогам внешнеторговой деятельности Республики Абхазия за несколько последних лет темпы роста экспорта значительно превосходят на темпах роста импорта, что положительно сказывается на итоговых показателях торгового баланса страны.
Самым крупным внешним партнером Абхазии является РФ, доля которой составляет более 70 % всего товарооборота. Далее идет Турция, Китай, Бразилия, Греция, Армения, а также Украина и Республика Беларусь.
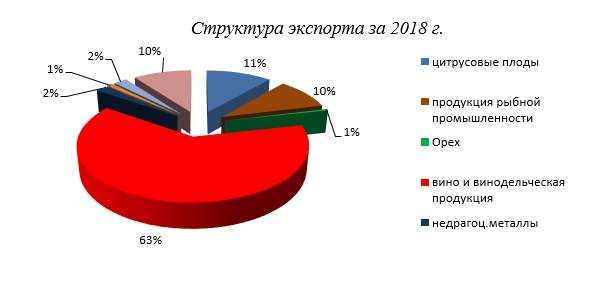
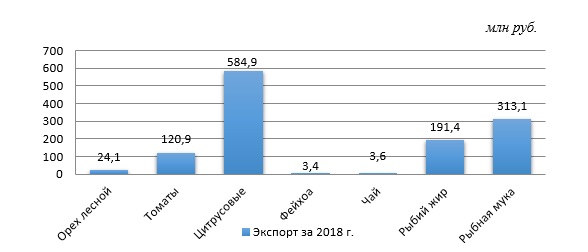
В списке экспортируемой из Абхазии продукции, которая главным образом попадает на рынки РФ и Турции традиционно превалирует продукция агропромышленного комплекса, добывающей и перерабатывающей промышленности. Среди нее можно выделить такие категории товаров как: винодельческая продукция, рыба и рыбопродукты, цитрусовые плоды, орехи, минералы и т.д.
Наиболее значительные в структуре импорта занимают такие категории как: продукты питания, строительные материалы, минеральные продукты, оборудование, бытовая техника, автотранспортные средства и прочие товары.
Природные ресурсы Абхазии
Абхазия – богатейшая в плане природных ресурсов страна. Республика располагает запасами каменного угля (более 5,3 млн. тонн), торфа, мрамора, гранита, известняка, габбро-диабазов, мела, туфа, барита, доломита, свинца, разнообразных стройматериалов. На шельфе Абхазии имеются небольшие месторождения нефти и газа. По предварительным данным, запасы нефти составляют от 300 до 500 миллионов тонн. Большая часть нефтяных запасов залегает на расстоянии в 10 километров от береговой линии. Имеются также небольшие месторождения газа.
Общая площадь земель сельскохозяйственного назначения - 421,6 тыс. га.
По водообеспеченности Абхазия занимает одно из первых мест в мире: на квадратный километр территории приходится более 1,7 млн. куб. м. речного стока в год. Общая длина 120 рек — более 5 тыс. км. В основном это стремительные горные потоки, что является потенциалом развития малой гидроэнергетики.
Лесом покрыто 57 % территории (497 тыс. га); оценка общего запаса лесонасаждений составляет 114,5 млн куб. метров.
Абхазия обладает колоссальным объёмом рекреационных ресурсов. Около 200 пансионатов, домов отдыха, санаториев, гостиниц, детских оздоровительных баз расположено во всех климатических зонах — от субтропической до альпийской. Имеется более 120 термальных и минеральных источников.
